Fraysseix–Rosenstiehl's planarity criterion
In graph theory, a branch of mathematics, Fraysseix–Rosenstiehl's planarity criterion is a characterization of planarity based on the properties of the trémaux tree defined by a depth-first search. It is named after Hubert de Fraysseix and Pierre Rosenstiehl.
Considering any depth-first search of a graph G, the edges encountered when discovering a vertex for the first time define a DFS-tree T of G. The remaining edges form the cotree. Three types of patterns define two relations on the set of the cotree edges, namely the T-alike and T-opposite relations:
In the following figures, simple circle nodes represent vertices, double circle nodes represent subtrees. Twisted segments represent tree paths and curved arcs represent cotree edges (with label of the edge put near the curved arc). In the first figure, 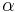 and
and 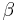 are T-alike (it means that their low extremities will be on the same side of the tree in every planar drawing); in the next two figures, they are T-opposite (it means that their low extremities will be on different sides of the tree in every planar drawing).
are T-alike (it means that their low extremities will be on the same side of the tree in every planar drawing); in the next two figures, they are T-opposite (it means that their low extremities will be on different sides of the tree in every planar drawing).
- Let G be a graph and let T be a DFS-tree of G. The graph G is planar if and only if there exists a partition of the cotree edges of G into two classes so that any two edges belong to a same class if they are T-alike and any two edges belong to different classes if they are T-opposite.
See also
References
- H. de Fraysseix and P. Rosenstiehl, A depth-first search characterization of planarity, Annals of Discrete Mathematics 13 (1982), 75–80.